Investing in bonds? You’ll want to know about yield and return.
Yield is a general term that relates to the return on the capital you invest in a bond. Price and yield are inversely related: As the price of a bond goes up, its yield goes down, and vice versa.
There are several definitions that are important to understand when talking about yield as it relates to bonds: coupon yield, current yield, yield-to-maturity, yield-to-call and yield-to-worst.
Let's start with the basic yield concepts.
- Coupon yield, also known as the coupon rate, is the annual interest rate established when the bond is issued that does not change during the lifespan of the bond.
- Current yield is the bond's coupon yield divided by its current market price. If the current market price changes, the current yield will also change.
For example, if you buy a $1,000 bond at par (often described as “trading at 100,” meaning 100 percent of its face value) and receive $45 in annual interest payments, your coupon yield is 4.5 percent. If the price goes up and the bond subsequently trades at 103 ($1,030), then the current yield will fall to 4.37 percent.
Current yield matters if you plan to sell your bond before maturity. But if you buy a new bond at par and hold it to maturity, your current yield when the bond matures will be the same as the coupon yield.
Key Terms
Coupon and current yield only take you so far down the path of estimating the return your bond will deliver. For one, they don't measure the value of reinvested interest. They also aren't much help if your bond is called early—or if you want to evaluate the lowest yield you can receive from your bond. In these cases, you need to do some more advanced yield calculations. The following yields are worth knowing, and you can find them using FINRA’s Fixed Income Data.
Yield to maturity (YTM) is the overall interest rate earned by an investor who buys a bond at the market price and holds it until maturity. Mathematically, it is the discount rate at which the sum of all future cash flows (from coupons and principal repayment) equals the price of the bond. YTM is often quoted in terms of an annual rate and may differ from the bond’s coupon rate. It assumes that coupon and principal payments are made on time. It does not require dividends to be reinvested, but computations of YTM generally make that assumption. Further, it does not consider taxes paid by the investor or brokerage costs associated with the purchase.
Yield to call (YTC) is figured the same way as YTM, except instead of plugging in the number of months until a bond matures, you use a call date and the bond's call price. This calculation takes into account the impact on a bond's yield if it is called prior to maturity and should be performed using the first date on which the issuer could call the bond.
Yield to worst (YTW) is whichever of a bond's YTM and YTC is lower. If you want to know the most conservative potential return a bond can give you—and you should know it for every callable security—then perform this comparison.
Interest rates regularly fluctuate, making each reinvestment at the same rate virtually impossible. Thus, YTM and YTC are estimates only, and should be treated as such. While helpful, it's important to realize that YTM and YTC may not be the same as a bond's total return. Such a figure is only accurately computed when you sell a bond or when it matures.
Figuring Bond Return
If you've held a bond over a long period of time, you might want to calculate its annual percent return, or the percent return divided by the number of years you've held the investment. For instance, a $1,000 bond held over three years with a $145 return has a 14.5 percent return, but a 4.83 percent annual return.
When you calculate your return, you should account for annual inflation. Calculating your real rate of return, as it is often referred to, will give you an idea of the buying power of your earnings in a given year. You can determine real return by subtracting the inflation rate from your percent return. As an example, an investment with 5 percent return during a year of 3 percent inflation is usually said to have a real return of 2 percent.
To figure total return, start with the value of the bond at maturity (or when you sold it) and add all of your coupon earnings and compounded interest. Subtract from this figure any taxes and any fees or commissions. Then subtract from this amount your original investment amount. This will give you the total amount of your total gain or loss on your bond investment. To figure the return as a percent, divide that number by the beginning value of your investment and multiply by 100:

Reading a Yield Curve
You've probably seen financial commentators talk about the Treasury Yield Curve when discussing bonds and interest rates. It's a handy tool because it provides, in one simple graph, the key Treasury bond data points for a given trading day, with interest rates running up the vertical axis and maturity running along the horizontal axis.
A typical yield curve is upward sloping, meaning that securities with longer holding periods carry higher yield.
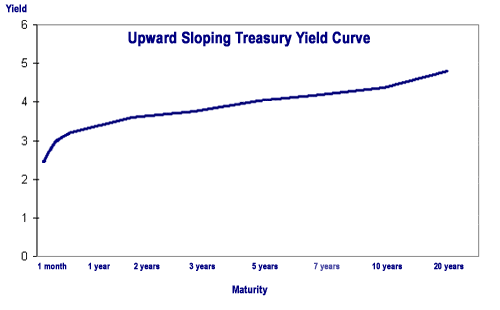
In the yield curve above, interest rates (and also the yield) increase as the maturity or holding period increases—yield on a 30-day T-bill is 2.55 percent, compared to 4.80 percent for a 20-year Treasury bond—but not by much. When an upward-sloping yield curve is relatively flat, it means the difference between an investor’s return from a short-term bond and the return from a long-term bond is minimal. In such a situation, investors would want to weigh the riskof holding a bond for a long period versus the only moderately higher interest rate increase they would receive compared to a shorter-term bond.
A real-world application of the Treasury Yield Curve is that it serves as the benchmark for the vast majority of mortgage rates. Mortgage interest rates typically follow the yield of the 10-year U.S. Treasury very closely. In fact, they have moved in tandem for more than 30 years.
The Department of Treasury provides daily Treasury Yield Curve rates, which can be used to plot the yield curve for that day.
Learn more about bonds.